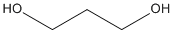
In general terms, a spacer is introduced into an oligonucleotide to add distance between the oligonucleotide and a modifier. This reduces the possibility of any adverse interaction between the modifier and the sequence. For instance, G-rich sequences are known to quench fluorescein therefore the use of a suitable spacer will remove the dye label from the proximity of the oligonucleotide minimising the quenching effect. In a similar fashion, spacers are often used to distance between multiple additions of self-quenching dyes e.g. fluorescein.(1) The application of the modified oligonucleotide will dictate whether a hydrophilic (Spacer 18 (HEG), Spacer 9 (TEG)) or hydrophobic spacer (Spacer C2, C3, C6, C12, C16) is required. Multiple incorporations of varying lengths of these spacers allow the precise length of the spacer arm to be controlled. This can be important in hairpin loop(2) and duplex studies(3) of DNA. Several spacers have specific uses. A C3 spacer mimics the three carbon spacing between the 3’ and 5’ hydroxyls of a sugar unit.(4) Although useful where the base at a specific site is unknown, the flexibility of the alkyl chain distorts the sugar-phosphate backbone. This can be alleviated with the use of dSpacer since incorporation of this modifier sits directly into the natural sugar-phosphate backbone with no adverse effect. This modifier mimics abasic sites(5) and is useful in the study of mutations resulting from depurination. Although less common than terminal spacing, but equally important, spacers have been incorporated within an oligonucleotide.
This adds distance between sections of the sequence. For instance, Cytocell’s SMART detection assay(6) uses spacer 18 in the template probe where one section acts as an anchor in binding to the target leaving the other section free for hybridisation to the extension probe to allow amplification during PCR. In this case, the spacer gives flexibility to the template probe to enable hybridisation to both the target and the extension probe. In similar way, spacer 18 is used in Scorpion™ Primers to separate the probe and primer section. However in this case, this not only provides the flexibility to allow the probe to flip back to hybridise to the amplicon but also acts as a PCR blocker to prevent read through to the probe.(7) 3'-Spacers are often used as an alternative to 3'-phosphate as blockers since, when incorporated at the 3'-end, the resulting oligonucleotide shows nuclease and polymerase resistance. In fact, spacer C3 is often incorporated at the 3'-end of an oligonucleotide for use with restriction enzymes rather than phosphate since the latter is thought to partially cleave during the assay.
Ref:
- See for example: Design of multidye systems for FRET-based applications, M.S. Shchepinov and V.A. Korshun, Nucleosides, Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids, 20, 369-374, 2001.
- Circular dichroism studies of an oligodeoxyribonucleotide containing a hairpin loop made of a hexaethylene glycol chain: conformation and stability, M. Durand, K. Chevrie, M. Chassignol, N.T. Thuong and J.C. Maurizot, Nucleic Acids Research, 18, 6353-6359, 1990.
- A nicked duplex decamer DNA with a PEG6 tether, L. Kozerski, A.P. Mazurek, R. Kawecki, W. Bocian, P. Krajewski, E. Bednarek, J. Sitkowski, M. P. Williamson, A.J.G. Moir and P.E. Hansen, Nucleic Acids Research, 29, 1132-1143, 2001.
- Enhancing sequence-specific cleavage of RNA within a duplex region: Incorporation of 1,3-propanediol linkers into oligonucleotide conjugates of serinol-terpyridine, B.N. Trawick, T.A. Osiek and J.K. Bashkin, Bioconjugate Chem., 12, 900-905, 2001.
- (a) Oligodeoxynucleotides containing synthetic abasic sites model substrates for DNA-polymerases and apurinic apyrimidinic endonucleases, M. Takeshita, C.N. Chang, F. Johnson, S. Will and A.P. Grollman, J. Biol. Chem., 262, 10171-10179, 1987; (b) NMR-studies of abasic sites in DNA duplexes deoxyadenosine stacks into the helix opposite the cyclic analog of 2-deoxyribose, M.W. Kalnik, C.N. Chang, A.P. Grollman and D.J. Patel, Biochemistry, 27, 924-931, 1988.
- Detection of virus mRNA within infected host cells using an isothermal nucleic acid amplification assay: marine cyanophage gene expression within Synechococcus sp, S.D. Wharam, M.J. Hall and W.H. Wilson, Virology Journal, 4, 52-59, 2007.
- Duplex Scorpion primers in SNP analysis and FRET applications, A. Solinas, L.J. Brown, C. McKeen, J.M. Mellor, J.T.G. Nicol, N. Thelwell and T. Brown, Nucleic Acids Research, 29 (20), e96, 2001.
|
Synthesizer
|
Column
|
Type/Description
|
Notes
|
|
MerMade 6,12
|
MerMade, syringe (all scales)
|
Pipette type column
|
A MerMade column is also known as a Supercolumn
|
|
MerMade 4, 48X, 96E, 192E, 192X
|
MerMade, Syringe (up to 1.3 mL)
|
Pipette type column
|
A MerMade column is also known as a Supercolumn
|
|
ABI 384 / 394
|
Luer
|
Barrel column with luer fitting at either end
|
Also known as ALL-FIT or Standard
|
|
Expedite 8909
|
Luer
|
Barrel column with luer fitting at either end
|
Also known as ALL-FIT or Standard
|
|
ABI3900
|
MerMade
|
Pipette type column
|
A MerMade column is also known as a Supercolumn
|
|
K&A H4, H8, H8SE, H2, H32, H64
|
Luer
|
Barrel column with luer fitting at either end
|
Also known as ALL-FIT or Standard
|
|
K&A S4CL/S8CL
|
Luer
|
Barrel column with luer fitting at either end
|
Also known as Standard. For this instrument, we recommend the Luer (Standard) column as the ALL-FIT columns have a wider barrel.
|
|
Dr Oligo 48
|
MerMade
|
Pipette type column
|
A MerMade column is also known as a Supercolumn
|
|
Dr Oligo 192XLc, 768XLc just plates
|
MerMade, Syringe (up to 1.3 mL)
|
Pipette type column
|
A MerMade column is also known as a Supercolumn
|
|
OligoMaker X12, 48, 192, X192, X96
|
MerMade, Syringe (up to 1.3 mL)
|
Pipette type column
|
A MerMade column is also known as a Supercolumn
|