Ribonuclease R (RNase R)
Product Details
ShowRibonuclease R from E. Coli includes the following components based on size:
250 units:
12.5 μL of the RNase R enzyme and 250 μL of the optimised 10X Reaction Buffer containing 0.2 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 1 M KCl, and 1 mM MgCl2.
2500 units:
125 μL of the RNase R enzyme and 2.5 mL of the optimised 10X Reaction Buffer containing 0.2 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 1 M KCl, and 1 mM MgCl2.
Product is always in stock with fast shipping guaranteed, if purchased today the order will be shipped out the next business day (Next day shipping applies for US customers only).
Ribonuclease R (RNase R)
Ribonuclease R (RNase R), 250 Units
Ribonuclease R (RNase R) from E. coli is a magnesium-dependent 3ʹ to 5ʹ exoribonuclease available for circular RNA cleanup, alternative splicing research, and gene expression studies.
Key features
Show-
Efficacy and quality assured under ISO 13485 certification
-
Available in bulk and for custom configurations
-
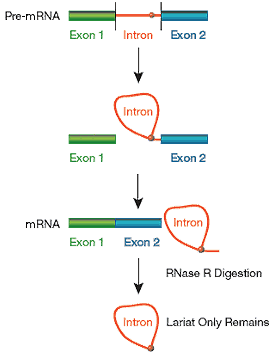
Effectively degrades linear RNA, Y-structure RNAs, but not lariat loops or circular RNAs.
-
Digests linear RNAs to enrich for circular RNAs used for protein production or intronic cDNA library construction.
Product information
Concentration: 20 U/ μL
Unit Definition: One unit of RNase R converts 1 µg of poly(A) into acid-soluble nucleotides in 10 minutes at 37 °C under standard assay conditions.
Storage Buffer: RNase R is supplied in a 50% glycerol solution containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 100 mM NaCl, 0.1 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, and 0.1% Triton® X-100.
RNase R 10X Reaction Buffer: 0.2 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 1 M KCl, and 1 mM MgCl2.
SDS
-
10X RNase R Reaction Buffer English EU
-
10X RNase R Reaction Buffer English US
-
RNase R English EU
-
RNase R English US
Manuals and user guides
Access support
Need some support with placing an order, setting up an account, or finding the right protocol?
Contact us